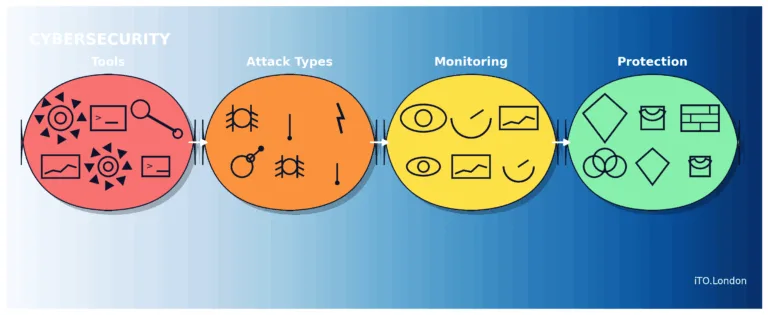
Practical Cyber Security:
Attacks, Tools, Monitoring, Defence

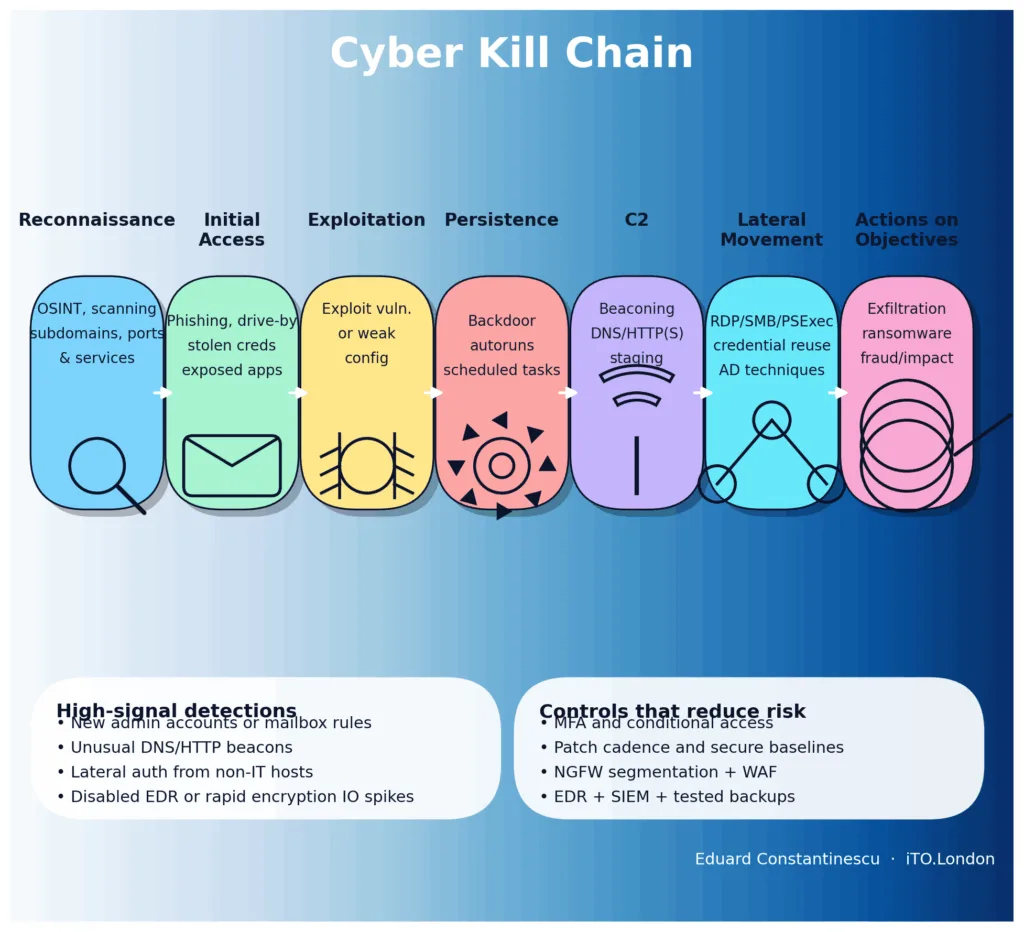
[Recon] —>
[Initial Access] —>
[Execution] —>
[Lateral Move] —>
[Impact/Exfil]
Info-gather
Nmap, OSINT
Phishing, BEC,
rive-by, Web vulns
ZAP, Burp, SQLMap
Exploits,
Metasploit,
Cobalt Strike
Cred abuse,
pivoting tools,
PS remoting …
Ransomware,
DDoS, Data theft
============== DEFENCE LAYERS ==============
Identity, MFA, email security
Okta or Entra ID, Proofpoint
Network and perimeter
NGFW, Segmentation, IDS/IPS
Palo Alto, Suricata/Snort
Process and hygiene
Least privilege, patching,
asset inventory, logging
EDR/XDR on endpoints
Defender, CrowdStrike
Web and DNS protection
Cloudflare WAF, DNS filter
Umbrella or equivalent
Vulnerability management
Nessus, OpenVAS, SLAs
Backup, immutability
3-2-1 rule
Monitoring and response
SIEM, SOAR, UEBA
Sentinel, Splunk, QRadar
Incident response
Runbooks, drills
tabletop exercises
In day-to-day IT you do not win with buzzwords; you win with basics done well, repeatable, and measured. In a day-to-day you don’t get all these, but in 30 years of IT, you will experience most of them.
This post is the simple map when thinking about CyberSecurity, threats, testing, monitoring, and defence.
Attack types – short definitions
Backdoor Trojan – malicious access planted for later entry. First fix: rebuild and rotate credentials, close egress, hunt for persistence.
Birthday attack – collision trick against hashes. Fix: modern hashing (SHA-256+), signed artefacts.
Brute force attacks – trial of many passwords/keys. Fix: MFA, lockouts, throttling.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) – social engineering to move money. Fix: payment verification out-of-band, DMARC, impersonation protection.
Code injection – untrusted input executed as code. Fix: input validation, parameterised queries, WAF rules.
Cross-site scripting (XSS) – hostile script in the browser. Fix: output encoding, CSP, WAF, secure frameworks.
Cryptojacking – your compute mined for crypto. Fix: EDR, block unknown outbound, monitor CPU spikes.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) – overwhelm services. Fix: edge DDoS protection (Cloudflare), autoscale, rate limits.
DNS spoofing – fake DNS answers. Fix: DNSSEC, trusted resolvers, TLS everywhere.
DNS tunnelling – data hidden in DNS queries. Fix: block unusual DNS, inspect, alert on entropy.
Drive-by attacks / downloads – silent infection from a page. Fix: patch browsers, script controls, EDR.
Eavesdropping – sniffing traffic. Fix: TLS 1.2+, HSTS, network segmentation.
Identity-based attacks – abusing accounts/tokens. Fix: conditional access, MFA, least privilege, short-lived tokens.
Insider threats – malicious or careless insiders. Fix: logging, DLP, approvals, separation of duties.
IoT attacks – weak devices at the edge. Fix: isolate VLANs, change defaults, patch or replace.
Malware – any hostile software. Fix: EDR + allow-listing + patching cadence.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) – intercept/alter traffic. Fix: TLS, certificate pinning, secure Wi-Fi.
Password attacks – guessing/reuse/dumps. Fix: MFA, SSO, password managers, breach matching.
Phishing – broad fraud emails. Fix: secure email gateway, user training, report button.
Ransomware – encrypt and extort. Fix: EDR, immutable backups, tested restores, least privilege.
Session hijacking – steal cookies/tokens. Fix: secure cookies, token binding, short expiry, re-auth.
Spear-phishing – targeted phishing. Fix: VIP protection, domain monitoring.
Spoofing -pretending to be someone/something. Fix: SPF, DKIM, DMARC, display name defence.
SAML-related attacks (your list had “SaL!”, assuming SAML) – token forgery/relay. Fix: strict audience/issuer, signed/encrypted assertions.
SQL Injection – untrusted input in SQL. Fix: parameterised queries, ORM, WAF.
Supply-chain attacks – compromise via third parties. Fix: SBOM, signed builds, least-privileged integrations.
Trojan horses – malware disguised as legit. Fix: allow-listing, user education, EDR.
URL manipulation / interpretation – tamper query/paths. Fix: server-side checks, deny-by-default routing.
Web attacks (general) – file upload abuse, auth bypass, logic flaws. Fix: secure coding, WAF, threat modelling.
Whaling – phishing aimed at execs. Fix: exec training, VIP mail rules.
Zero-day exploits – unknown vulns used now. Fix: hardening, exploit mitigations, virtual patching/WAF.
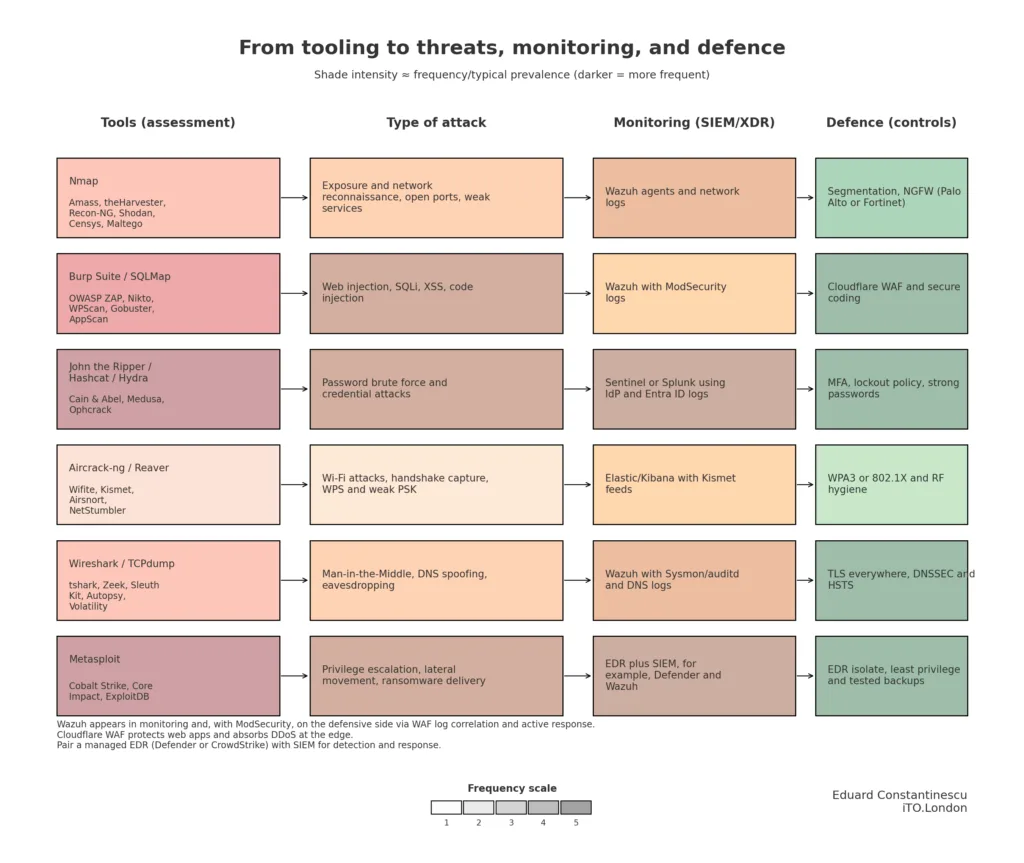
Assessment & offensive tooling – what each does and the easy way to start
Information gathering / recon:
Nmap – port/service discovery. Easy start:
nmap -sV -T4 <target>Amass – subdomain discovery. Start:
amass enum -d example.comtheHarvester – emails/domains via OSINT. Start:
theHarvester -d example.com -b allRecon-NG – modular recon framework. Start: init workspace, run marketplace modules.
Shodan / Censys – internet-wide device search. Start: query by org, IP range, product.
Maltego – graph relationships. Start: seed with domain, run transforms.
Credentials / password testing:
John the Ripper – offline crack hashes. Start:
john --wordlist=rockyou.txt hashes.txtHashcat – GPU cracking. Start:
hashcat -m 3200 hashfile wordlistHydra / THC-Hydra – online brute-force. Start:
hydra -l user -P passlist ssh://hostMedusa – parallel login tests.
Cain & Abel (legacy) – LAN capture, decode.
Ophcrack – rainbow table Windows hashes.
Web application assessment:
Burp Suite – proxy, scanner, repeater. Start: intercept, crawl, active scan.
OWASP ZAP – open-source scanner/proxy. Start: “Quick Start → Automated Scan”.
Nikto – fast web misconfig scan. Start:
nikto -h https://siteSQLMap – exploit SQLi. Start:
sqlmap -u "https://site?id=1" --batchWPScan – WordPress vulns. Start:
wpscan --url https://siteGobuster – brute force dirs/DNS. Start:
gobuster dir -u https://site -w wordlist
Exploitation frameworks:
Metasploit – modules, payloads, post-ex. Start:
msfconsole→search→use→runCore Impact / Cobalt Strike – commercial post-ex/teams.
Exploit-DB – public exploit catalogue.
Wireless:
Aircrack-ng – capture/attack WPA handshakes.
Wifite – wraps common attacks.
Kismet – passive wireless IDS.
Airsnort / NetStumbler (legacy) – WEP discovery.
Reaver – targets WPS.
Vulnerability scanning:
Nessus – broad vuln scanner with templates.
OpenVAS – open-source vuln scanning.
Nexpose – Rapid7 scanner.
Lynis – Unix hardening audits.
Retina (legacy/limited use) – Windows scanning.
AppScan – web/app testing (commercial).
Packets & forensics:
Wireshark – packet capture/analysis. Start: capture filter
host <IP>; use profiles.TCPdump / tshark – CLI capture. Start:
tcpdump -i eth0 -nnvvSleuth Kit / Autopsy – disk forensics.
Volatility – memory forensics.
Foremost / Binwalk / Guymager – carving, firmware analysis, imaging.
Social engineering tooling:
GoPhish – run phishing campaigns safely.
SocialFish / HiddenEye – phishing frameworks (use responsibly, test only).
Evilginx / EvilURL – reverse proxy & IDN look-alikes (lab only).
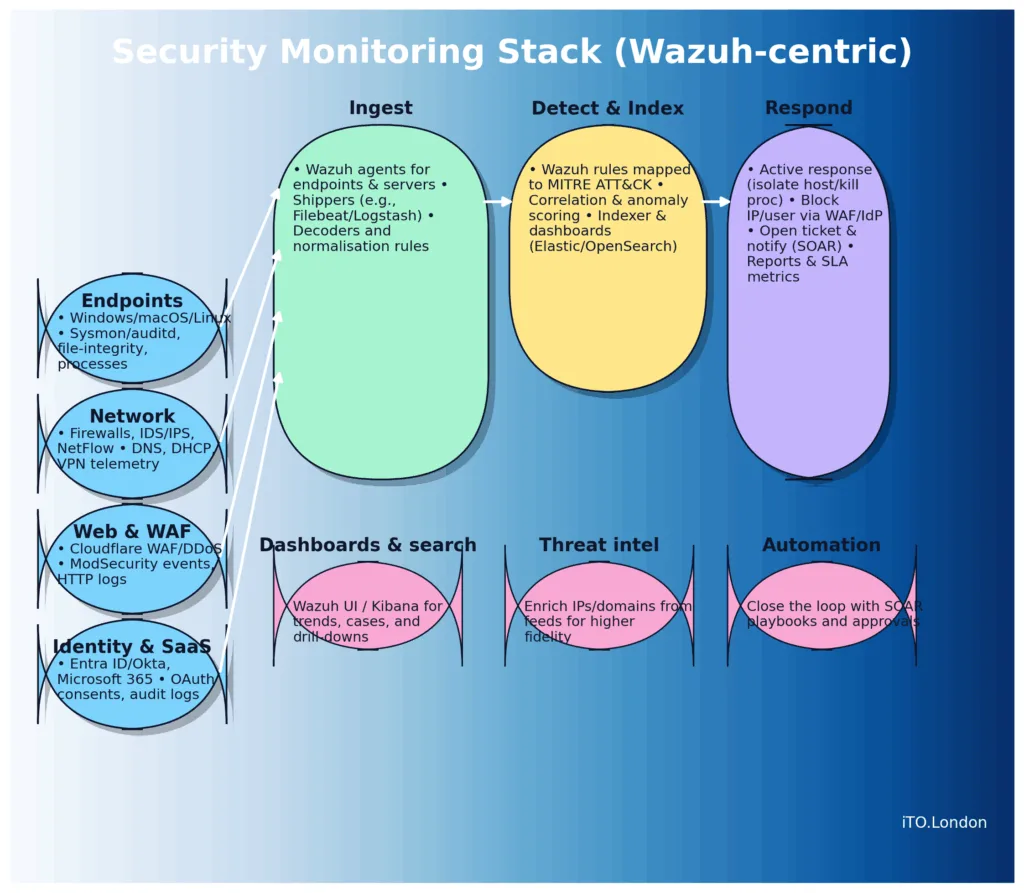
Monitoring (SIEM/XDR) – the 1st five I think the most
Wazuh: open-source SIEM/XDR with agents (Windows/macOS/Linux), FIM, rootkit and vuln detection, MITRE mapping, active response. Self-host or managed.
Microsoft Sentinel: cloud SIEM with native M365/Defender/Azure signals and KQL analytics.
Splunk Enterprise Security: powerful search and correlation at scale; costly at volume but strong content.
IBM QRadar: mature rules and offence model, wide connector support.
Elastic Security (ELK): search-first, scalable, more DIY tuning than the above.
Quick wins: forward endpoint logs, DNS logs, and WAF logs; enable Sysmon/auditd; start with high-signal rules (admin changes, lateral movement, impossible travel, disabled EDR, unusual DNS, web attacks).
Defensive controls – what I know and used
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: DR/XDR across Windows, macOS, Linux, mobile; strong m365 integration.
CrowdStrike Falcon: EDR with high-quality detections and managed threat hunting options.
Palo Alto Networks / Fortinet NGFW: segmentation, IPS, app control; put east-west and north-south traffic behind policy.
Cloudflare WAF + DDoS: protect apps at the edge; managed rules, bot controls, rate limiting.
Wazuh + ModSecurity: host IDS + WAF log correlation; curate alerts and use active response for rapid containment.
Foundations that reduce 80% of pain: MFA everywhere (if possible), least privilege, patch cadence, secure baselines, backups that are truly restorable, documentation and clean inventories.

